shoulder posterior labral tear test|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff : white label The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). .
web27 de set. de 2023 · Baixar Cyberpunk 2077 & Phantom Liberty Bundle – v2.0 + All DLCs + Bonus Content + REDmod Torrent Bluray 720p | 1080p | 4k 2160p Dual search .
{plog:ftitle_list}
1,384 Followers, 1,861 Following, 398 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Federal Sports (@federalsports) 1,384 Followers, 1,861 Following, 398 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Federal Sports (@federalsports) Something went wrong. There's an issue and the page could not be .
Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder. Treatment may be nonoperative or operative depending on chronicity of symptoms, .Diagnosing a posterior labral tear of the shoulder can be difficult for physicians. These tears can present with a wide variety of symptoms and there are multiple physical exam tests of undetermined significance.
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at the back of the shoulder joint. SLAP tear: A superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear occurs at the top of the glenoid (shoulder socket) and extends from the front to the back, where the .
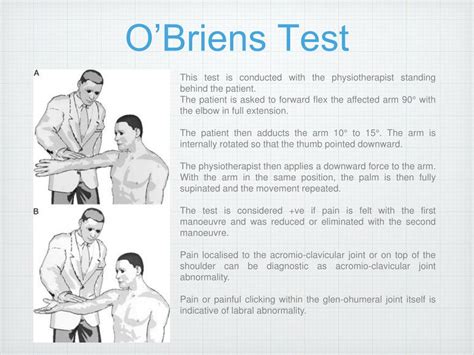
The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2]The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). .
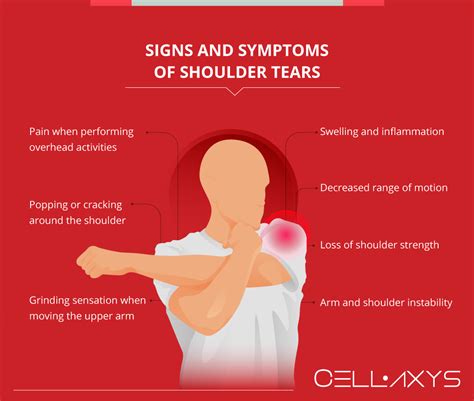
Posterior instability of the shoulder can be assessed by using a simple test. 11 With the patient supine or sitting, the examiner pushes posteriorly on the humeral head with the patient's arm. The most common symptoms of a shoulder labrum tear are shoulder pain, instability and, in some cases, a feeling of grinding, locking or catching while moving the shoulder. These symptoms may vary depending on .
A shoulder labrum tear is a tear of the labral cartilage that lines the shoulder joint. Get detailed information about labral tears, including SLAP tears and Bankart tears, shoulder labral tear symptoms, diagnostic tests, and .
Microtrauma is an important factor in the development of instability due to the repetitive shearing forces and loads to the posterior shoulder in the flexed, adducted, and interally rotated position.Microtrauma can lead to degeneration . Get detailed information about labral tears, including SLAP tears and Bankart tears, shoulder labral tear symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment, including surgery. . (superior labrum from anterior to posterior) .Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum.They involve the superior glenoid labrum, where the long head of biceps tendon inserts. They may extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral .A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. . The term SLAP stands for superior labrum anterior and posterior. . The results of these physical tests will .
Posterior Labral Tear Neurovascular Disorders . performed by flexing shoulder to 90°, flex elbow to 90°, and forcibly internally rotate driving the greater tuberosity farther under the CA ligament. . Posterior Stress Test. positive if there is pain and sense of instability with the maneuver. technique. Place the patient's arm in flexion .

Five points Heat Seal Tester vendor
speed's test vs o'brien's
97% sensitive for posterior labral tear when combined with a Kim test Kim test performed by having the patient seated, arm at 90° abduction, followed by flexing the shoulder to 45 forward flexion while simultaneously applying axial load on the elbow & posterior-inferior force on the upper humerus. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
Posterior labral tear. The SLAP tear can continue posteriorly and can contribute to posterior shoulder pain. In some cases the posterior labral tear can form a flap valve and a cyst will develop. This cyst can also cause posterior shoulder pain, and when it is large, it can compress the suprascapular nerve, causing weakness of shoulder rotation.This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . Guanche CA, Jones DC. Clinical testing for tears of the glenoid labrum. Arthroscopy. 2003;19:517-523. Liu SH, Henry MH, Nuccion S, Shapiro MS, Dorey F . Type 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Type 3: Torn labrum tissue is caught in the .
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK The Porcellini Test appears to be a highly valid test to assess for posterior labral tears in the shoulder.G.
Posterior shoulder dislocation: . A “clunk” sound or clicking sensation can indicate a labral tear even without instability. 12. . A reliable and simple test for posterior instability of .The accuracy of the jerk test in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion was the following: sensitivity, 73%; specificity, 98%. The Kim test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly inferior labral lesion, whereas the jerk test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly posterior labral lesion. Sudden pain in the shoulder denotes a positive test. Kim et al. reported a 97% sensitivity for detecting posterior instability when both the jerk test and Kim test were positive. Evaluation. Plain Radiographs. . In the setting of a posterior labral tear, treatment generally consists of arthroscopic labral repair with suture anchors with or .
Posterior Labral Repair Rehabilitation Protocol (Arthroscopic or Open) 0-2 weeks post-op: Goals . • Shoulder sub-maximal (pain free) isometrics with sling/immobilizer in all directions: flexion, . For throwing athletes: perform isokinetic testing below (if available). If passes test, begin interval throwing program. Re-test monthly until .Explanation of O'Brien's Test in orthopedic shoulder examination including involved tissues, test postion, test movement, etc. plus video demonstration. . superior labral tear from anterior to posterior). A false positive may occur if there is an injury to the rotator cuff . indicates pathology at that joint while pain felt ‘deeper’ in .
Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of .
To perform this test both the elbow and the shoulder should be flexed at 90°. The examiner must support the arm of the patient at the level of the elbow so that the upper extremity can be as much relaxed as possible. . The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the margins of the glenoid fossa. It stabilizes the shoulder joint . posterior labrum tear: Injuries to the back of the shoulder joint can cause a posterior labrum tear. These are rare and make up only 5 to 10 percent of all shoulder injuries. Symptoms of a labral tear
special tests for shoulder labrum
When the tear is at the back of the shoulder ( posterior ) (6 o'clock to 11 o'clock), it is a Reverse Bankart tear : . When a tear is a combination of Bankart , Reverse Bankart tear and SLAP tear , it is known as a 270 degree tear: . Chronic, longstanding labral tears can give rise to paralabral cysts.This is where the tear becomes a one-way valve so joint synovial fluid seeps out of the . Posterior Labral Tear Neurovascular Disorders . generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and biceps tendonitis. . "peel back" test shows "peel back" of the labrum with 90° of external rotation and abduction.Shoulder special tests can be useful for evaluating and diagnosing shoulder pathology such as impingement, biceps tenonopathy, instability, rotator cuff tears, and injury to the labrum. These are some of the most common shoulder special tests performed in .
The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous complex that attaches as a rim to the articular cartilage of the glenoid fossa. Its role is to deepen and increase the surface area of the glenoid (acting as a static stabiliser of the glenohumeral joint); resist anterior and posterior movement and assist with blocking shoulder dislocation and subluxation at the maximal ranges of motion.Evidence [edit | edit source]. A systematic review of the validity and accuracy of clinical tests used to detect labral pathology of the shoulder showed the +LR of the Jerk Test to be LR 34.71 and the -LR to be 0.27. The reported diagnostic accuracy for the jerk test was a sensitivity of 73% and specificity of 98%. References [edit | edit source]We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. . On the posterior aspect, the labrum is dimensionally square but with a rounded distal surface. The functions of the acetabular labrum are: Joint stability; . Patrick test - For assessment of the posterior labrum. The patient's hip is flexed and then .
The glenoid labrum is integral to shoulder stability and can be difficult to assess clinically. Whilst it is a single anatomical structure, damage to different regions results in very different clinical manifestations. . Compared to the superior labrum and anterior labrum, there are very few described tests for posterior labral lesions, .
Shore Hardness Tester vendor
1. Instruct students to join the game with one of the following methods: A. Visit play.blooket.com and enter the 7-digit game code. B. Scan the QR code with their .
shoulder posterior labral tear test|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff